There are essentially 3 technologies behind a digital camera. They are:
Lights are supposed to be directed onto a sensor to reproduce the image. Each colour of lights has different wavelengths. If the lens cannot direct lights accurately onto the sensor, there will be imperfections, which adversely affect the sharpness and colour accuracy of the produced picture.
Canon is able to correct the various aberrations by producing aspherical lens that are made from fluorite or UD glass lens. She has also devised a system of positioning additional lenses with unique shapes in strategic places to eliminate additional aberrations that might occur during the zooming process.
Aspherical lens can reproduce images more accurately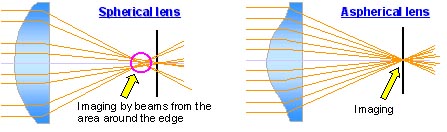
The CCD is a monochrome device. It needs a colour filter to produce a colour image. Each primary colour (eg red, green and blue) is placed on an individual pixel. The coloured filter then filters out all but the chosen colours for that pixel. The camera then combines the coloured pixel with its neighbouring pixels to produce the final image.
Traditionally, images are produced using traditional cyan-yellow-green-magenta colour filter. However, they are generally lacking details and intensity. Canon has overcome this shortcoming by using a green-red-green-blue filter, which produces richer and more natural colours.
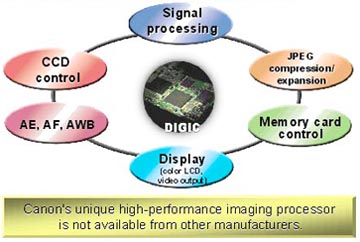
With several new algorithms added, DIGIC gives stunning image quality, super-fast processing speed with large-capacity buffering and low power consumption.

How stunning image quality is achieved?
DIGIC ensures that no noise (Tiny white dots or streaks in pictures) is created when the image is captured and gives a wider dynamic range (range between brightest and darkest part of an image).
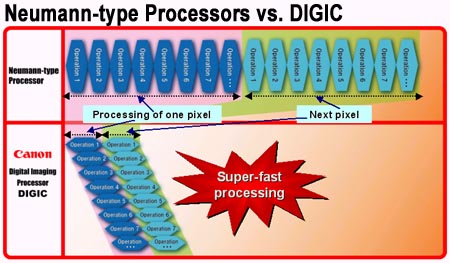
How super fast processing speed with large-capacity buffering is achieved.
Being a "dedicated" processor for digital camera, DIGIC has a shorter processing time. Therefore images are saved into a memory card at a fast speed, thus freeing the buffer capacity of the digital camera and allowing more shots to be taken.

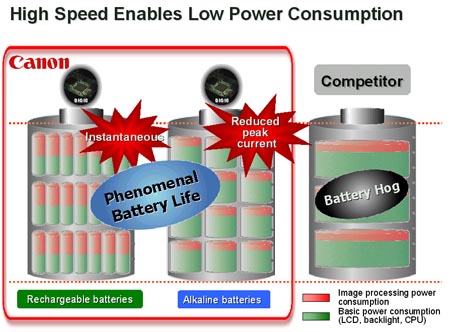
How Low power consumption is achieved?
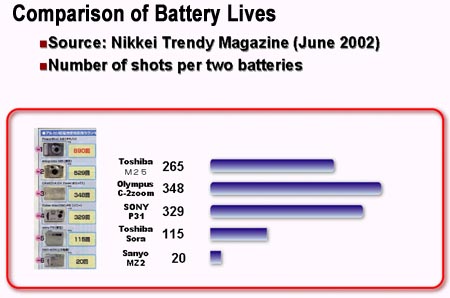
Because of the fast processing speed, the digital cameras consume lesser power and batteries last longer when compared with competitors.
Intelligent Scene Analysis based on Photographic Space - iSAPS helps determine more accurate camera settings
Canon has accumulated a vast amount of photographic know-how to determine the type of settings needed to best capture an image. This experience is built into a database.
When the automatic mode on the camera is switched on, the camera will analyse the scene. Then it will refer to this database to determine the best camera setting (eg amount of exposure, the type of lighting, size of aperture) that will best express the image. This proprietary technology is known as iSAPs
Click here to read more about technology.